In every organization, problems are an inevitable part of daily operations. Whether it’s a hiccup in the production line, a customer complaint, or an unexpected setback, problems arise constantly, demanding attention and resolution. However, how organizations approach and solve these problems can often make the difference between stagnation and growth. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the art and science of problem solving within organizations, exploring common issues and effective strategies for tackling challenges head-on by developing problem solving capability.
The Problem with Problem Solving
Before delving into solutions, let’s address some common issues that plague the problem-solving process in many organizations:
1. Focusing on Certification over Capability
Many organizations prioritize certifications and formal qualifications over actual problem-solving skills. This emphasis on credentials can lead to a workforce ill-equipped to tackle real-world challenges effectively.
2. Overreliance on Tools
Using the same problem-solving tool for every issue is akin to treating every problem as a nail because you only have a hammer. Organizations often fall into the trap of relying solely on one approach, such as A3, without considering whether it’s the most suitable for the problem at hand.
3. Failure to Address Root Causes
Merely containing problems without digging deeper to identify and address root causes is a recipe for recurring issues. Without addressing underlying issues, organizations find themselves grappling with the same problems repeatedly.
4. Neglecting PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act)
Jumping straight to solutions without following a structured problem-solving process like PDCA can lead to ineffective or short-term fixes. Without a systematic approach, organizations risk implementing solutions that fail to address the core issue.
5. Leadership Overload
When leaders attempt to solve every problem themselves, they become overwhelmed and unable to focus on coaching and developing their teams. This reactive approach results in leaders firefighting rather than empowering their teams to tackle challenges autonomously.
6. Lack of Skill and Time
Inadequate problem-solving skills coupled with time constraints can prolong the resolution process, leading to frustration and inefficiency. Understanding problem-solving theory is not enough; individuals must also be able to apply it effectively in real-world situations.
7. Failure to Capture and Visualize Problems
Without a mechanism for capturing and visualizing problems, organizations struggle to prioritize and address issues systematically. This lack of visibility can lead to problems slipping through the cracks and going unresolved.
Four Types of Problems
Not all problems are created equal, and organizations must tailor their approach to the specific type of problem at hand. Art Smalley’s framework categorizes problems into four types:
- Type 1 – Troubleshooting: Addressing unexpected or reactive problems.
- Type 2 – Gap from Standard: Dealing with deviations from established norms or standards.
- Type 3 – Target Condition: Pursuing proactive improvements toward predefined objectives.
- Type 4 – Open-Ended: Tackling complex or novel challenges that defy easy categorization.
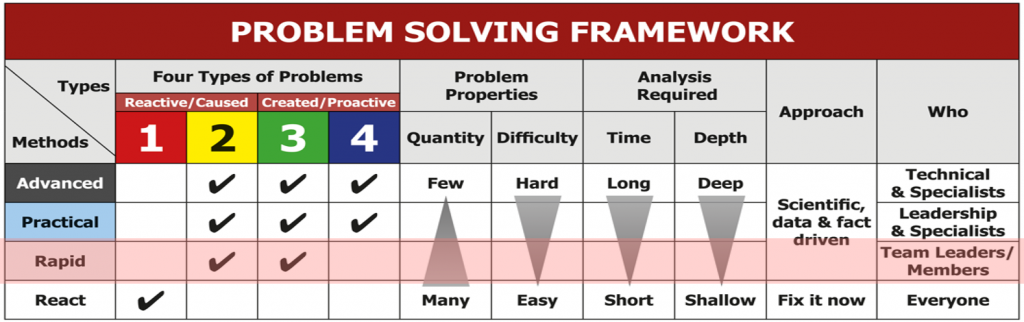
Each problem type requires a different approach and level of analysis, from rapid problem solving for straightforward issues to practical problem solving for more complex and strategic challenges. Being aware of the differences enhances problem solving capability.
Problem Solving: Purpose, Process and People
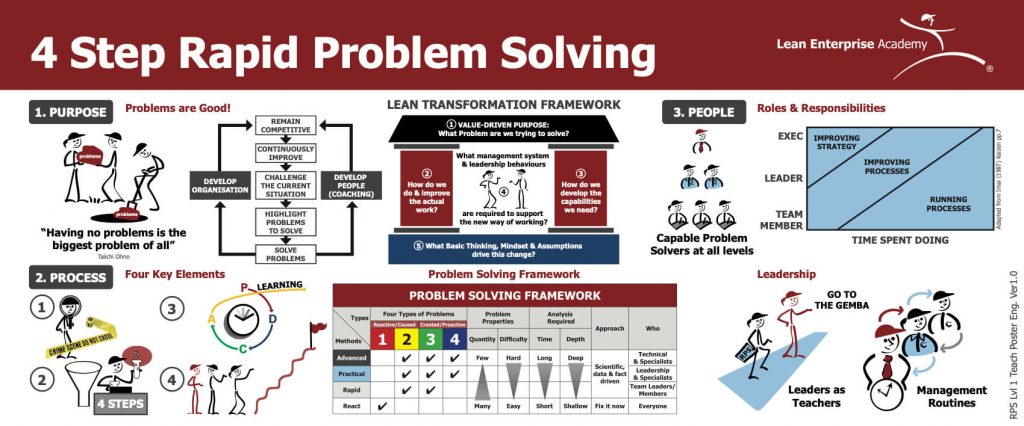
At the heart of effective problem solving lies a clear understanding of its purpose and significance within the organization. Rather than viewing problems as obstacles to be avoided, organizations should recognize them as opportunities for growth and development. Taiichi Ohno’s famous quote, “Having no problems is the biggest problem of all,” underscores the importance of embracing challenges as catalysts for improvement.
By addressing problems systematically, organizations not only enhance their operational efficiency but also foster a culture of continuous learning and development. Moreover, problem solving serves as a vehicle for both organizational and individual growth, enabling employees to acquire new skills and competencies while driving business success.
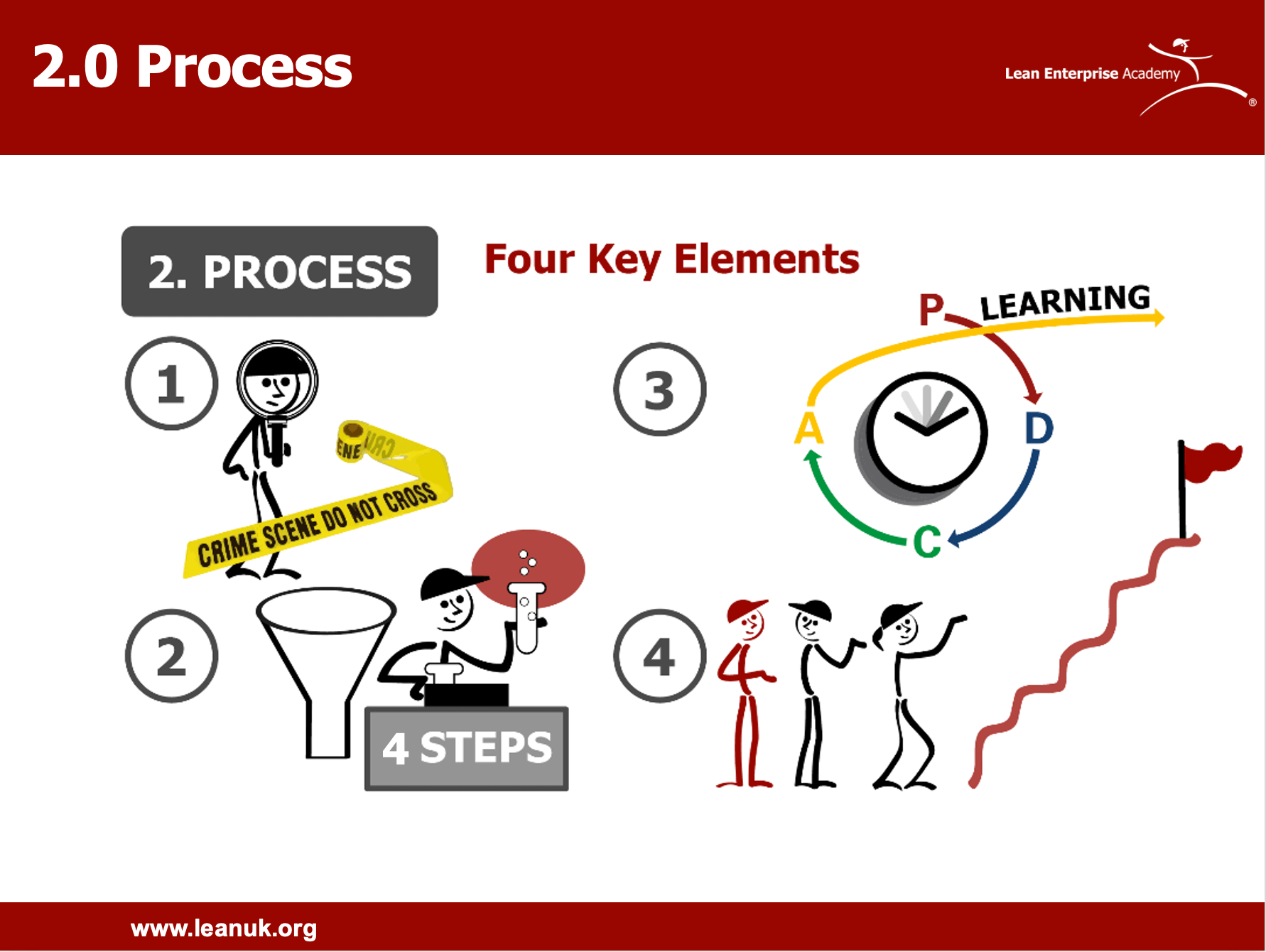
Process: Key Elements of Problem Solving
Effective problem solving entails several key elements, including:
- Go and See: Proactively seeking out problems and gathering firsthand information to inform decision-making.
- Scientific Approach: Applying a structured and data-driven methodology, such as PDCA, to systematically address problems.
- PDCA Thinking: Embracing a mindset of continuous improvement and iteration to drive organizational learning.
- Ultimate Goal: Maintaining a clear focus on the desired outcomes and objectives of problem-solving efforts.
People: Roles and Responsibilities in Problem Solving
Effective lean problem solving is not solely the responsibility of a select few (that’s a key difference between lean and six sigma) but rather a collective effort that engages individuals at all levels of the organization. By fostering a culture of problem solving and empowerment, organizations can unlock the full potential of their workforce and drive sustainable improvement.
Leaders play a critical role in nurturing problem-solving capabilities throughout the organization, from frontline teams to top executives. By allocating time and resources to coaching and development, leaders can cultivate a cadre of skilled problem solvers capable of driving continuous improvement and innovation.
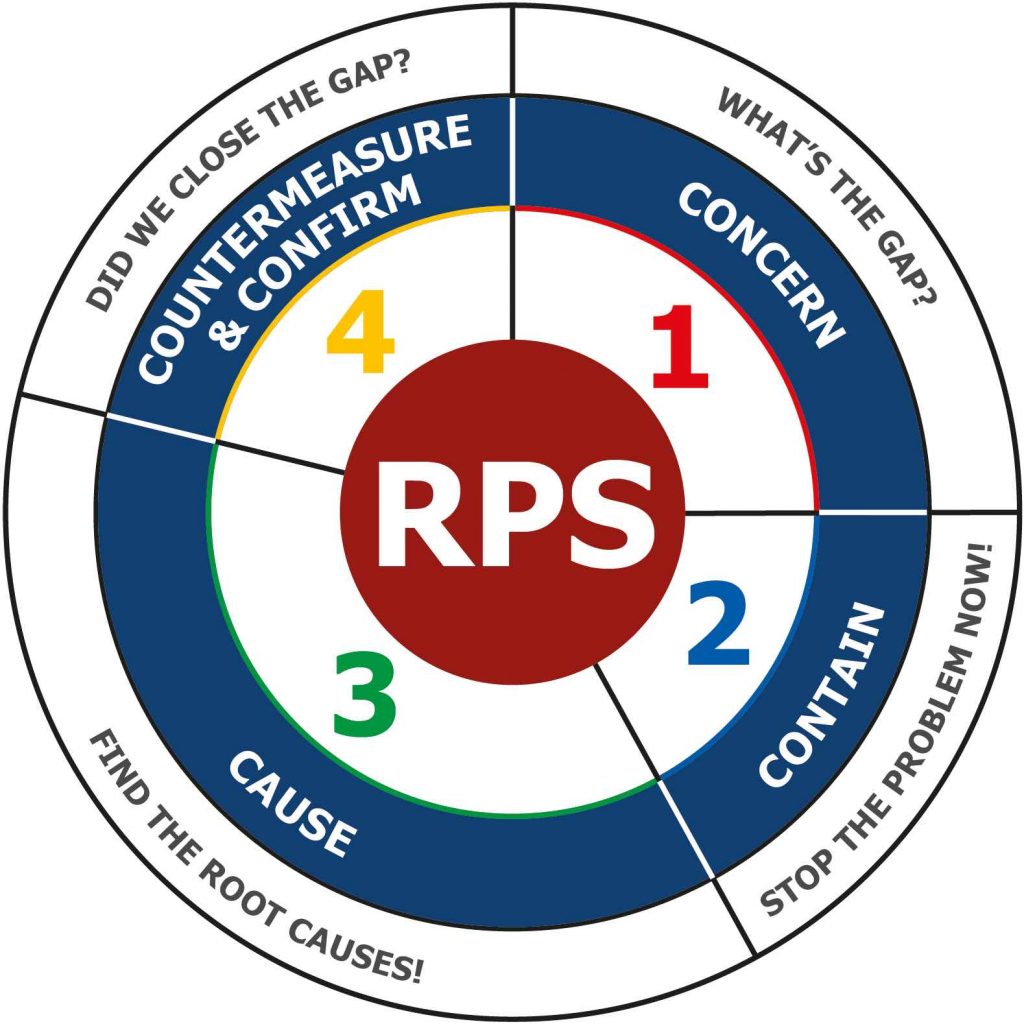
Rapid Problem Solving Method: A Closer Look
The rapid problem-solving method offers a structured approach to addressing challenges quickly and effectively. With its focus on concern, containment, cause, countermeasure, and check, this method provides a simple yet powerful framework for problem solving at all levels of the organization.
Each step of the rapid problem-solving method serves a specific purpose, from clarifying the problem to identifying root causes, developing countermeasures, and evaluating results. By following this systematic approach, organizations can streamline their problem-solving efforts and achieve sustainable improvements in performance and efficiency.
A Learning Journey: Mastering Problem Solving Skills
Mastering problem-solving skills requires a systematic and iterative approach to learning and development. Organizations can facilitate this process through structured training programs, hands-on exercises, and real-world problem-solving projects.
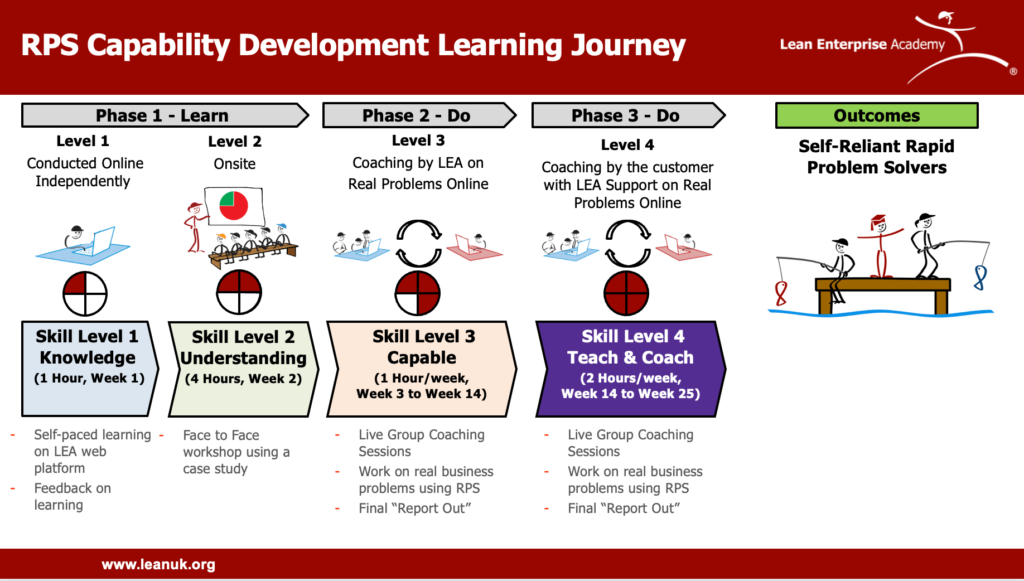
The RPS Capability Learning Journey developed with Hologic provides an illustration of an integrated approach to developing capability and self-reliance. The “Skill Level 1 – Knowledge” part of the learning process is conducted online using LEA’s Lean Learning Journey platform. “Skill Level 2 – Understanding” is a 4 hour session using a case. This can be carried out onsite or broken into 1 hour sessions online as the case is part of our online learning platform. “Skill Level 3 – Capable” uses remote group coaching sessions, working on real business problems. The process used is shown in the table below:
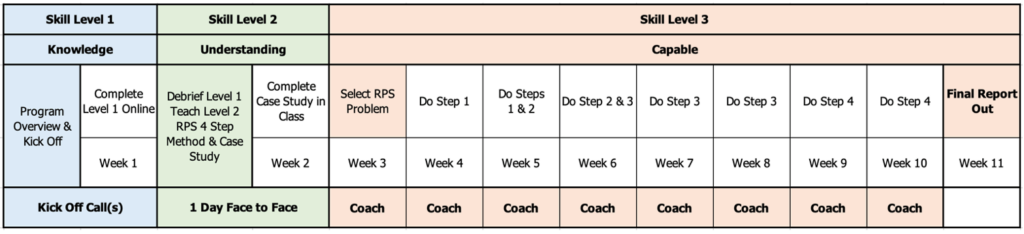
We shared the process during the Lean Global Connection event in November 2023. Here is a level 3 report out showing a real problem that was solved while teaching the RPS process.
Finally a co-hort of the people that progressed through levels 1 to 3 go on to develop the ability to teach and coach their colleagues. This results in the organisation developing self-reliance to use the process internally themselves.
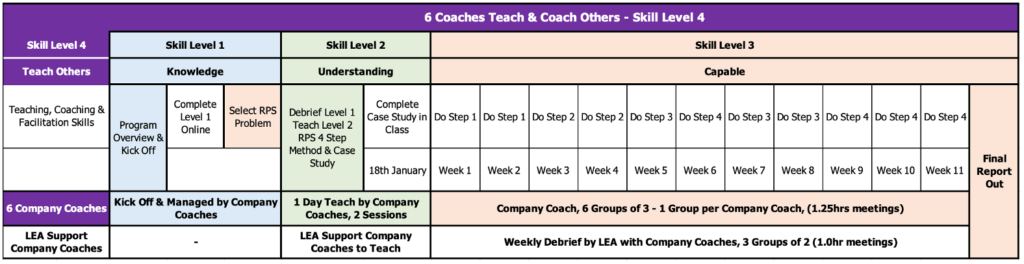
By providing employees with the tools, resources, and support they need to excel in problem solving, organizations can foster a culture of continuous improvement and innovation. From online courses to live coaching sessions and interactive workshops, there are myriad opportunities for individuals to enhance their problem-solving capabilities and drive organizational success.
Conclusion
Effective problem solving is not just a technical skill but a mindset and a culture that permeates every level of an organization. By adopting a structured approach to problem solving capability, nurturing problem-solving capabilities, and providing ongoing support and development, organizations can unlock new opportunities for growth, innovation, and success.
In today’s fast-paced and dynamic business environment, the ability to solve problems quickly and effectively is more critical than ever. By mastering the art and science of problem solving, organizations can navigate challenges with confidence and emerge stronger and more resilient than ever before.
You can learn how several organisations are developing problem solving capability at our UK Lean Summit in April.