Process – What are key aspects to A3 Practical Problem Solving?

Process Teach Point Video
Watch Video in full screen mode when possible

Key Learning Points
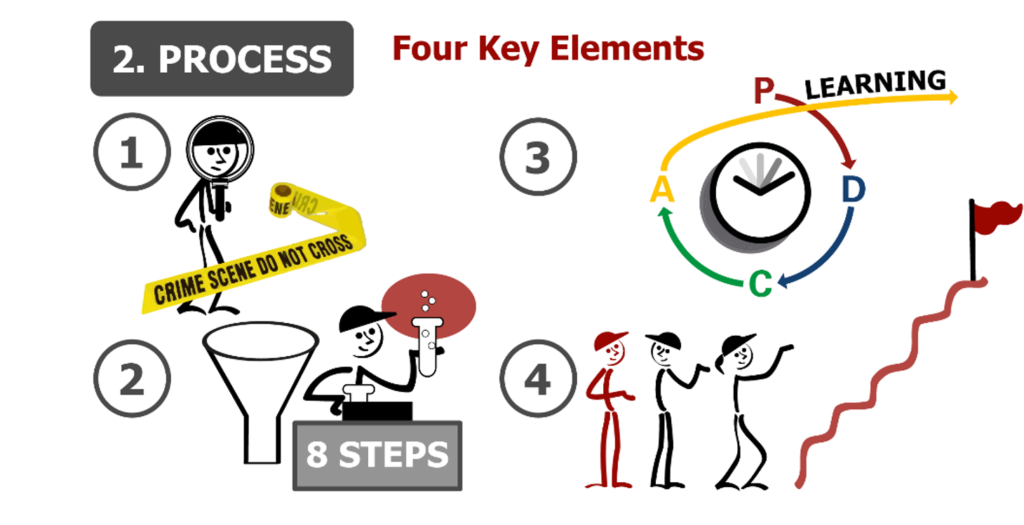
Key Learning Points from Video
1 – “Go and See” at the workplace – grasp the real situation.
2 – Follow Structured Scientific Method – not guessing. In Practical Problem Solving it is 8 Steps.
3 – Follow Plan – Do – Check – Act an approach of rapid trials and tests to prove out theories and learn.
4 – Take a step towards where we ultimately want to be (One problem at a time.)
The fundamental thinking basis for Problem Solving is Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA)

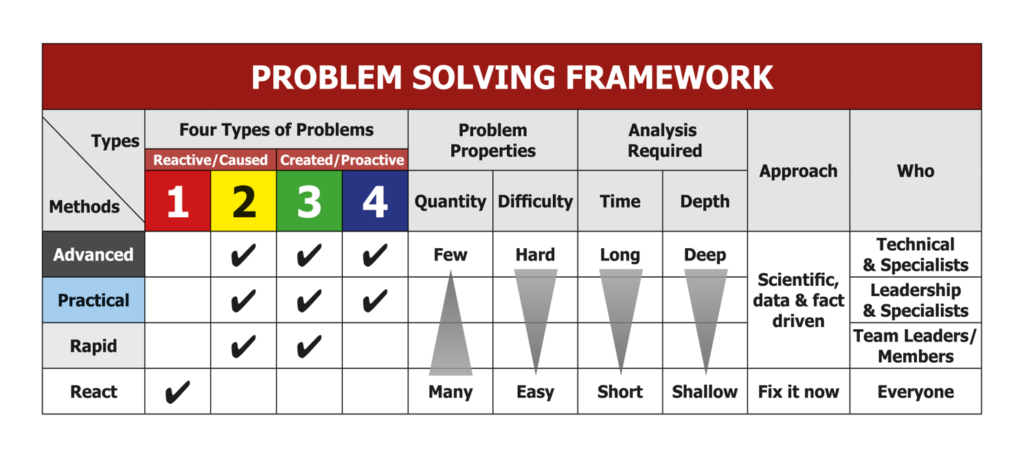
Problem Solving Framework
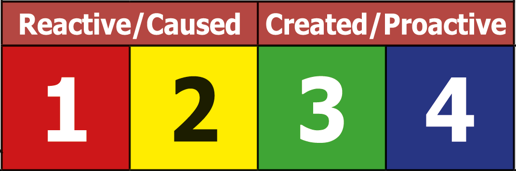
Types of Problems

Not one size or problem solving approach fits all as there are different Types of Problems.
Art Smalley’s Book describes Four Main Types of Problems as:
Type 1 = Troubleshooting
Type 2 = Gap from Standard
Type 3 = Target Condition
Type 4 = Open Ended
If we understand the types of problems, we stand a better chance of applying an appropriate process to “solving” them. Thus we avoid the issues in the famous quote from Abraham Maslow, “I suppose it is tempting, if the only tool you have is a hammer, to treat everything as if it were a nail.”
Most business problems fall into four main categories (see the diagram below), each requiring different thought processes, improvement methods, and management cadences:
Before using a method to solve a problem you need to understand what type of problem you are trying to solve.
Need to consider the Type of Problems, their Properties, the Analysis required and Level in the organisation.
Otherwise you waste time and resource.
Problem Solving Methods

Reacting to an unexpected event – For Type 1 Troubleshooting
Typically lots of them in the day, easy to fix quickly and you don’t need to analyse them so much.
Like changing a flat tyre or putting out a fire, you just fix it now! Everyone can do this. Like reacting to Andon cord pulls on a moving assembly line.

A 4 Step approach based upon the fundamentals of: Concern, Contain, Cause, Countermeasure & Confirm to tackle one off or step change type gaps in the workplace (Type 2 & 3).
Generally taught by functional and team leaders to natural work teams
Problem solving thinking captured on a quadrant chart. Uses the 7 Problem Solving tools to support fast but structured approach to problem solving, designed for first line leaders – not experts or after extensive training. Simple visual tools are used to capture the thinking.

An 8 step problem solving approach taking the Rapid method further. For current and longer term business issues requiring more analysis to get to the root causes.
For Type 2 & 3 mainly although thinking way helps considerably with Type 4 problems.
Some problems need a little more time and deeper thinking in order to solve them. The root causes and countermeasures are not that straight forward or immediately obvious as in Rapid for example. Uses the 7 Problem Solving tools to support logical thinking.
Performed by Leaders and functional Specialists typically. A3’s are used to summarise the thinking, capture the story and share the learning.
React, Rapid and Practical can be used to tackle most problems encountered within the organisation ~ >90%.

Used for innovative problem solving to seek out new solutions. Achieves radical improvement, often a new product, process, system or value for the customer well beyond current levels.
Many different methods can be used but usually technical or specialist knowledge is required. These are infrequent, hard problems to solve typically.
For use on problems often with multiple drivers in play. Experimentation may be needed to learn and understand what is happening and what is needed.
Can take some time and deep analysis but the results can be a step change in performance.
“Organisations and individuals at all levels fall into this trap of having one primary or standard way of solving every problem,” said Smalley, who learned problem solving at Toyota’s historic Kamigo engine plant from Harada-san.
-
 Four Types of Problems£42.00
Four Types of Problems£42.00

Why Start with Practical Problem Solving ?
- Practical Problem Solving is a proven method based on Toyota’s 8 Step approach for developing people to solve problems.
- Practical Problem Solving enables Managers, Team leaders and Functional Specialists etc. to tackle most medium and mid complexity problems for their current and near term business challenges in their organisations.
- Once you have achieved level 3 capable skill in Practical Problem Solving, you should then be capable of the using the Rapid Problem Solving methods to work on the many small problems.
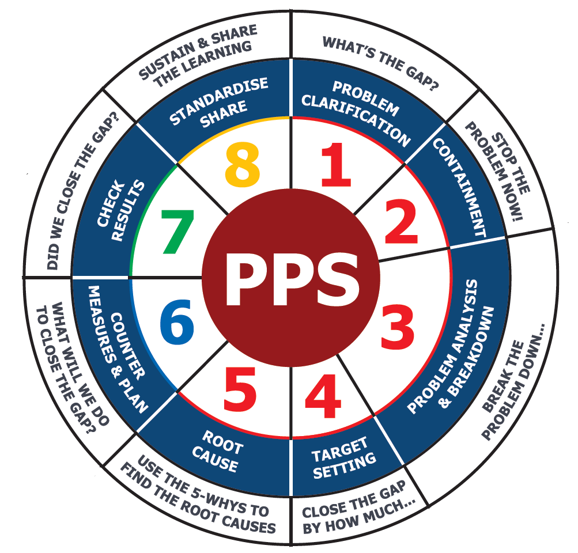
In the “Skill Level 2” course you will gain a deep Understanding of A3 8 Step Practical Problem Solving and learn how to visualise your problem solving story onto an A3 sized document.
Now move onto the next Topic.